Product Description
| MIC NO. | OEM.NO | APPLICATION | YEAR | PHOTO |
| TB34FI5711 | 351241 46755714 504086751 BMW : BMW : 1128171 BMW :T.v. BMW : BMW :T.v. BMW : BMW : BMW : BMW : BMW : 1433502 BMW : 171 BMW : 1742858T.v. BMW : 1745546 BMW : 1745546T.v. BMW : 7503424 BMW : 7515864 BMW : 7515865 BMW : 7563927 FIAT : 46755714 FIAT : 504T.v. FIAT : 504086751 FIAT : 504086751T.v. CHINAMFG : 504086751 CHINAMFG : 504086751T.v. LAND ROVER : PQGR571 MERCEDES-BENZ : 6112T.v. MERCEDES-BENZ : 6112T.v. MERCEDES-BENZ : 6112T.v. MERCEDES-BENZ : 6112 MERCEDES-BENZ : 6462R571 CHINAMFG : 1662R571T.v |
FIAT DUCATO Box (244_) 2.3 JTD FIAT DUCATO Box (250_, 290_) 110 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Box (250_, 290_) 120 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Box (250_, 290_) 120 Multijet 2,3 D 4×4 FIAT DUCATO Box (250_, 290_) 130 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Box (250_, 290_) 150 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Box (250_, 290_) 180 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Bus (244_) 2.3 JTD FIAT DUCATO Bus (250_, 290_) 110 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Bus (250_, 290_) 120 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Bus (250_, 290_) 130 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Bus (250_, 290_) 150 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Platform/Chassis (244_) 2.3 JTD FIAT DUCATO Platform/Chassis (250_, 290_) 110 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Platform/Chassis (250_, 290_) 120 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Platform/Chassis (250_, 290_) 120 Multijet 2,3 D 4×4 FIAT DUCATO Platform/Chassis (250_, 290_) 130 Multijet 2,3 D FIAT DUCATO Platform/Chassis (250_, 290_) 150 Multijet 2,3 D IVECO DAILY III Box Body/Estate 29 L 10 V (ALJA43A2, ALJA42A2, ALJA41A2) IVECO DAILY III Box Body/Estate 29 L 12 V (ALKA41A2, ALLA52A2, ALKA42A2) IVECO DAILY III Box Body/Estate 29 L 14 IVECO DAILY III Box Body/Estate 35 C 12 V, 35 S 12 V IVECO DAILY III Box Body/Estate 35 C 14, 35 S 14 IVECO DAILY III Box Body/Estate 35 S 10 (ANJA41A1, ANJA43A, ANJAV1A,… IVECO DAILY III Bus 35 S 12, 35 C 12, 40 C 12 IVECO DAILY III Platform/Chassis 29 L 10 (ALJAV1A1, ALJA41AA,…. IVECO DAILY III Platform/Chassis 29 L 12 (ALKA41A1, AHKA64A1, ALLA51A1) IVECO DAILY III Platform/Chassis 29 L 14 IVECO DAILY III Platform/Chassis 35 C 10 V , 35 S 10 V IVECO DAILY III Platform/Chassis 35 C 12 , 35 S 12 IVECO DAILY III Platform/Chassis 35 C 14, 35 S 14 IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 29L10 V IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 29L12 V, 29L12 V/P IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 29L14 C, 29L14 C/P, 29L14 V, 29L14 V/P IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 35C10, 35S10 IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 35C11 V, 35S11 V IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 35C12 V, 35C12 V/P, 35S12 V, 35S12 V/P IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 35C13 V, 35C13 V/P, 35S13 V, 35S13 V/P IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 35S14 C, 35S14 C/P, 35C14 V,… IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 40C10 V IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 40C11 V IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 40C12 V, 40C14 V/P IVECO DAILY IV Box Body/Estate 40C13 V, 40C13 V/P IVECO DAILY IV Bus 35S14, 35S14 /P IVECO DAILY IV Dump Truck 35C10 K IVECO DAILY IV Dump Truck 35C11 K, 35C11 DK, 35S11 K, 35S11 DK IVECO DAILY IV Dump Truck 35C12 IVECO DAILY IV Dump Truck 35C13 K, 35C13 DK, 35S13 K, 35S13 DK IVECO DAILY IV Dump Truck 35S14 K, 35S14 DK IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 29L10 IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 29L12 IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 29L14 IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 35C10, 35S10 IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 35C11, 35S11, 35S11 D, 35S11 /P IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 35C12, 35S12 IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 35C13, 35C13 /P, IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 35C14, 35S14, 35S14 /P IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 40C10 IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 40C11, 40C11 D IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 40C12 IVECO DAILY IV Platform/Chassis 40C13, 40C13 /P IVECO DAILY V Box Body/Estate 29L11 V, 35C11 V, 35S11 V, 40C11 V IVECO DAILY V Box Body/Estate 29L13 V, 35C13 V, 35S13 V, 40C13 V IVECO DAILY V Box Body/Estate 29L15 V, 35S15 V, 35C15L V, 40C15L V, IVECO DAILY V Dump Truck 35C11K, 35S11DKP IVECO DAILY V Dump Truck 35C13K, 35C13DKP IVECO DAILY V Platform/Chassis 26L11, 26L11D, 35C11D, 35S11, 40C11 IVECO DAILY V Platform/Chassis 29L13, 29L13D, 35C13D, 40C13 IVECO DAILY V Platform/Chassis 29L15 V, 35S15, 35C15L V, 40C15L V IVECO DAILY VI Box 33S11, 35S11, 35C11 IVECO DAILY VI Box 33S12, 35S12, 35C12 IVECO DAILY VI Box 33S13, 35S13, 35C13 IVECO DAILY VI Box 33S14, 35S14, 35C14 IVECO DAILY VI Box 33S15, 35S15, 35C15 IVECO DAILY VI Box 33S16, 35S16, 35C16 IVECO DAILY VI Box Body/Estate 33S12, 35S12 IVECO DAILY VI Box Body/Estate 33S14, 35S14 IVECO DAILY VI Box Body/Estate 33S16, 35S16 IVECO DAILY VI Platform/Chassis 33S11, 35S11, 35C11 IVECO DAILY VI Platform/Chassis 33S12, 35S12, 35C12 IVECO DAILY VI Platform/Chassis 33S13, 35S13, 35C13 IVECO DAILY VI Platform/Chassis 33S14, 35S14, 35C14 IVECO DAILY VI Platform/Chassis 33S15, 35S15, 35C15 IVECO DAILY VI Platform/Chassis 33S16, 35S16, 35C16 |
2002- 2011- 2006- 2571- 2011- 2011- 2015- 2002- 2011- 2006- 2011- 2011- 2002-2006 2011- 2006- 2571- 2006- 2011- 2002-2007 2002-2007 2005-2006 2002-2007 2005-2006 2002-2007 2003-2006 2002-2006 2002-2006 2005-2006 2002-2006 2002-2006 2005-2006 2006-2011 2006-2011 2006-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2006-2011 2006-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2006-2011 2007-2011 2011-2014 2011-2014 2011-2014 2011-2014 2011-2014 2011-2014 2011-2014 2011-2014 2014-2016 2016- 2014-2016 2016- 2014-2016 2016- 2016- 2016- 2016- 2014-2016 2016- 2014-2016 2016- 2014-2016 2016- |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Technical Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | One Year |
| Car Make: | FLAT |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What is the role of flat belt pulleys in agricultural machinery and equipment?
Flat belt pulleys play a crucial role in agricultural machinery and equipment, contributing to various operations and functions. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Flat belt pulleys are commonly used in agricultural machinery to transmit power from an engine or motor to different components. They serve as driving pulleys, connecting the power source to various agricultural implements and equipment such as threshers, pumps, conveyors, and grain elevators. The efficient power transmission facilitated by flat belt pulleys enables the proper operation of these agricultural machines.
2. Belt-Driven Systems:
Many agricultural machines utilize belt-driven systems, where flat belts and pulleys are employed to transfer power. These systems are cost-effective, easy to maintain, and provide smooth power transmission. Flat belt pulleys are key components in these systems, ensuring reliable power transfer and facilitating the movement of materials or the operation of specific agricultural processes.
3. Threshing and Harvesting:
In agricultural machinery such as threshers, flat belt pulleys are integral to the threshing and harvesting process. They drive the rotating mechanisms that separate grain or seeds from the crop plants. The pulleys provide the necessary power to rotate the threshing drum or cylinder, facilitating the separation of grain or seeds from the harvested crop.
4. Irrigation and Water Pumps:
Flat belt pulleys are utilized in agricultural equipment for irrigation and water pumping applications. They drive water pumps that draw water from wells, rivers, or other sources and distribute it for irrigation purposes. The pulleys transmit power from the engine or motor to the pump, enabling efficient water pumping and irrigation operations in agricultural fields.
5. Conveyor Systems:
Agricultural conveyor systems, used for tasks such as transporting crops, seeds, or harvested produce, often incorporate flat belt pulleys. The pulleys drive the conveyor belts, facilitating the movement of agricultural materials within the farm or processing facility. These conveyor systems are crucial for efficient material handling and sorting in agricultural operations.
6. Equipment Adjustability:
Flat belt pulleys offer adjustability in agricultural machinery and equipment. By using pulleys of different sizes or adjusting the pulley positions, the speed ratios and power transmission characteristics can be modified. This adjustability allows farmers and operators to optimize the performance of agricultural machines based on specific requirements, crop conditions, or operational preferences.
7. Versatility and Durability:
Agricultural environments can be demanding, with exposure to dust, moisture, and other challenging conditions. Flat belt pulleys are designed to be versatile and durable, capable of withstanding the rigors of agricultural applications. They are often constructed from materials such as cast iron or steel, ensuring longevity and reliable performance even in harsh agricultural settings.
Overall, flat belt pulleys play a vital role in agricultural machinery and equipment by facilitating efficient power transmission, driving essential components and processes, enabling adjustability, and ensuring the smooth operation of various agricultural operations.

How do flat belt pulleys handle different belt sizes and materials?
Flat belt pulleys are designed to accommodate different belt sizes and materials to ensure efficient power transmission. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Belt Sizes:
Flat belt pulleys are available in various sizes to match different belt widths and thicknesses. The width of the pulley’s groove is designed to provide proper contact and grip with the belt. Pulleys with wider grooves are used for wider belts, while narrower grooves are used for narrower belts. The pulley’s diameter may also vary depending on the specific application and power requirements.
2. Belt Materials:
Flat belt pulleys can handle a wide range of belt materials, including:
- Rubber: Rubber belts are commonly used due to their flexibility, high friction coefficient, and resistance to wear. They provide good grip and are suitable for most general-purpose applications.
- Polyurethane: Polyurethane belts offer high resistance to abrasion, oil, and chemicals. They are often used in applications that require superior performance and durability.
- Leather: Leather belts are known for their high strength and flexibility. They are used in applications where a certain level of slip is required or to transmit power in antique or vintage machinery.
- Nylon: Nylon belts are lightweight, have high tensile strength, and offer good resistance to wear and moisture. They are commonly used in applications that require low noise and high load capacity.
3. Belt Tensioning:
Flat belt pulleys should be designed with a tensioning mechanism to accommodate different belt sizes and maintain proper tension. This mechanism, such as an idler pulley or tensioning screw, allows for easy adjustment of the belt tension to ensure optimal power transmission and prevent slippage.
4. Belt Tracking:
To handle different belt sizes and materials, flat belt pulleys should be designed to provide proper belt tracking. This ensures that the belt stays within the pulley’s groove and maintains alignment during operation. Proper flanges or guides are often incorporated into the pulley design to prevent the belt from slipping off or wandering.
5. Material Compatibility:
The materials used in flat belt pulleys should be selected to be compatible with the specific belt materials. For example, if using a rubber belt, the pulley material should not cause excessive wear or damage to the belt’s surface. Compatibility between the pulley and the belt material helps ensure optimal performance and longevity.
By considering these factors, flat belt pulleys can effectively handle different belt sizes and materials, providing reliable power transmission in a wide range of applications.
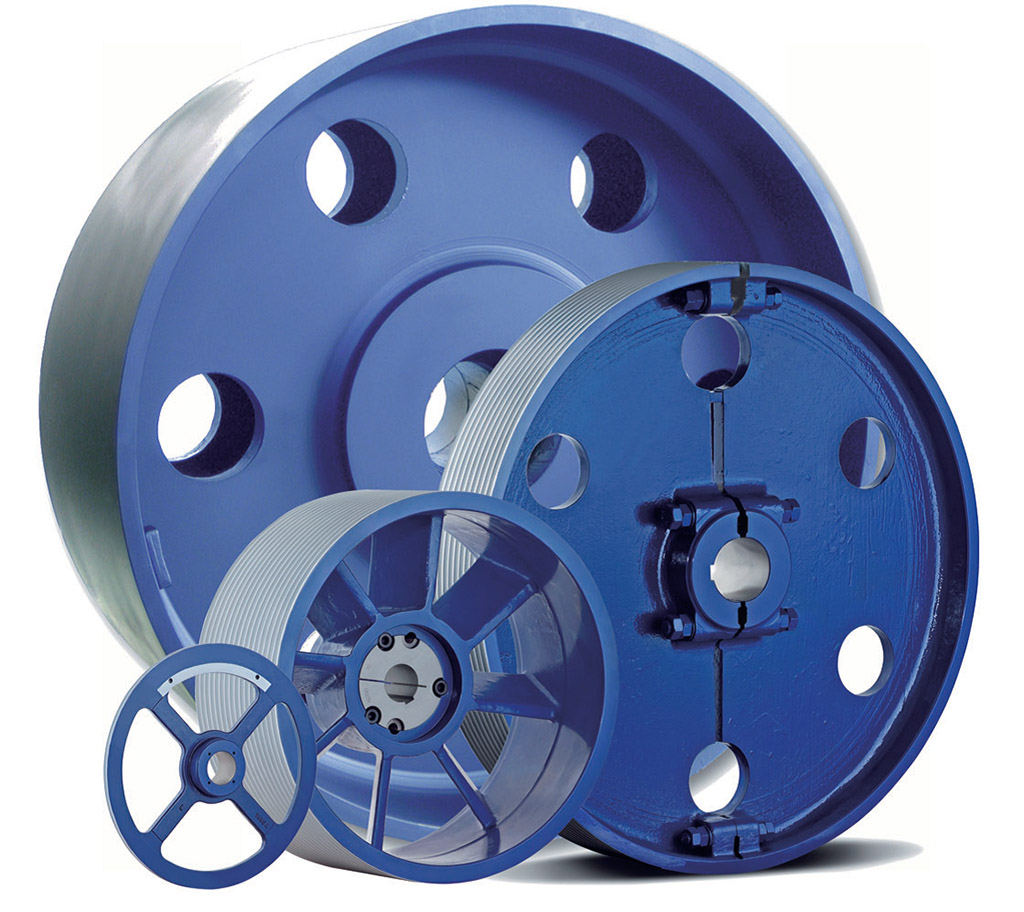

How do flat belt pulleys differ from other types of pulleys?
Flat belt pulleys have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of pulleys. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Belt Type:
The major difference lies in the type of belt used. Flat belt pulleys are specifically designed to work with flat belts, which are flexible and have a rectangular cross-section. In contrast, other types of pulleys, such as V-belt pulleys or timing belt pulleys, are designed for different belt profiles, such as V-shaped belts or toothed belts.
2. Belt Engagement:
Flat belt pulleys engage with the belt differently compared to other pulley types. The flat belt wraps around the pulley’s flat or slightly concave surface and relies on friction to transmit power. Other pulley types, like V-belt pulleys, have grooves that match the shape of the belt, providing positive engagement by fitting into the belt’s grooves.
3. Power Transmission:
Each pulley type is optimized for specific power transmission requirements. Flat belt pulleys are often used for applications that require relatively low power and moderate speeds. They are suitable for machinery that needs flexibility and ease of installation, making them commonly used in older machinery and certain industrial applications. Other pulley types, like V-belt pulleys or timing belt pulleys, offer advantages for high-power transmission, increased efficiency, or precise timing in applications such as automotive engines or industrial machinery.
4. Pulley Design:
Flat belt pulleys have a simple design, typically consisting of a cylindrical or disk-shaped body with a flat or slightly concave surface. Other pulley types may have more complex designs to accommodate specific belt profiles. For example, V-belt pulleys have grooves that match the V-shaped belts, while timing belt pulleys have toothed profiles that match the teeth on the timing belts.
5. Speed and Torque Conversion:
The design and configuration of pulleys, including flat belt pulleys, allow for speed and torque conversion. By varying the sizes of the pulleys, the speed and torque can be adjusted to meet the requirements of the machinery. However, the specific mechanisms for speed and torque conversion may differ between pulley types. For example, V-belt pulleys rely on the varying diameters of the pulleys to achieve speed conversion, while timing belt pulleys use the toothed profiles to ensure precise timing and synchronization.
6. Belt Tension and Alignment:
The methods used to maintain belt tension and alignment can also differ between pulley types. Flat belt pulleys often rely on adjustable pulley positions or tensioning mechanisms to achieve proper tension and alignment. Other pulley types may incorporate features like automatic tensioners or specialized tensioning systems to maintain optimal belt performance.
In conclusion, flat belt pulleys differ from other types of pulleys in terms of the belt type, engagement method, power transmission capabilities, design, speed and torque conversion mechanisms, as well as belt tension and alignment methods. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate pulley type for a given application.


editor by CX
2024-05-14