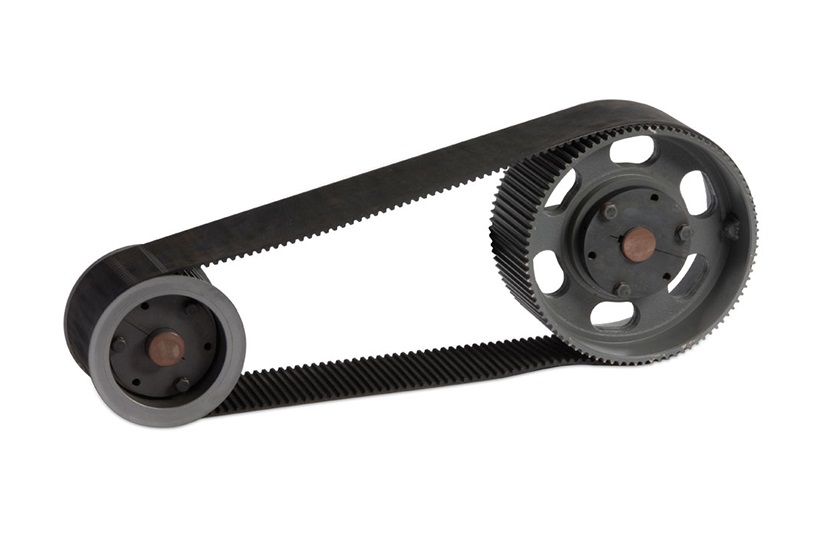
Product Description
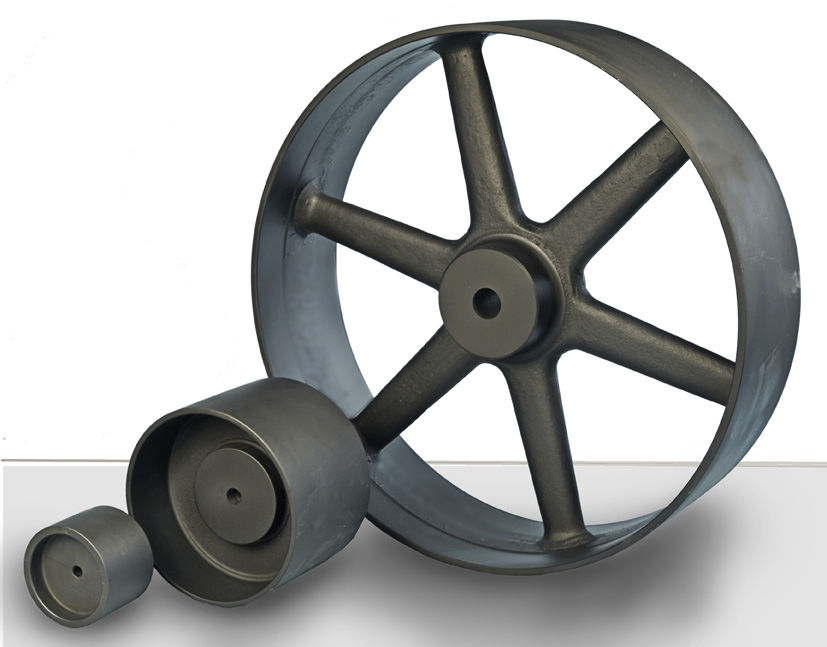
IHF S45C Stainless Steel Synchronous Blackening Timing Belt Pulley For New Energy Industry
Advantages:
1. Good quality products
2. Competitive prices
3. Fast delivery
4. Best after-sale service
5. Brand: HeFa or OEM/ ODM
6.Normal torque drive timing pulley:MXL/XL/L/H
7.High torque drive gear type: S2M/ S3M/ S5M/ S8M/ HTD3M /HTD5M/ HTD8M/P2M/P3M/P5M/P8M
8.High precision position drive gear type:2GT/3GT/5GT/8YU
9.Light load drive gear type:T5/T10
10.Heavy load drive gear type:AT5/AT10
Product Parameters
| Product | Timing Belt Pulley & idler pulley |
| Teeth type | Normal Torque Drive Type:MXL,XL,L,H,XH,XXH High Torque Drive Type:S2M,S3M,S5M,S8M,HTD2M,HTD3M,HTD5M,HTD8M,P2M,P3M,P5M,P8M High Precision Position Drive Type:2GT,3GT,5GT,8YU Light Load Drive Type:T5,T10,T20 Heavy Load Drive Type:AT5,AT10,AT20 |
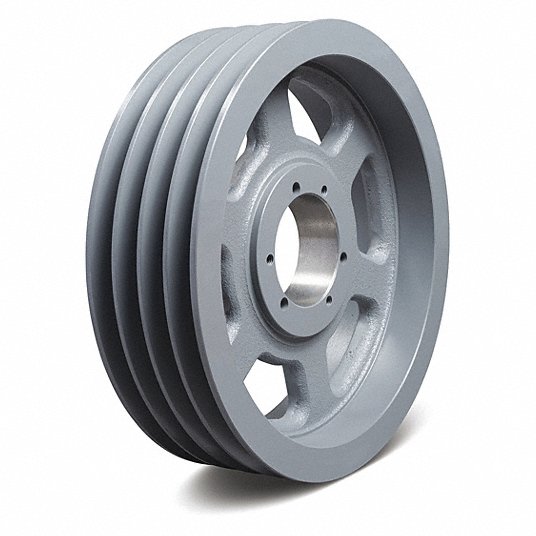
| Basic shape | Type A,Type B,Type D,Type E,Type F,Type K |
| surface treatment | Natural color anodizing,Black anodizing,Hard anodizing,Ni-plating,Blackening |
| Material | 6061(aluminum),S45C(45# steel),SUS304(Stainless steel) |
| Bore | Pilot bore, Taper bore and Customized bore. |
| testing equipment | projecting apparatus,salt spray test,durometer,and coating thickness tester,2D projector |
| producing equipment | CNC machine,automatic lathe machine,stamping machine,CNC milling machine,rolling machine,lasering,tag grinding machine etc. |
| Machining Process | Gear Hobbing, Gear Milling, Gear Shaping, Gear Broaching,Gear Shaving, Gear Grinding and Gear Lapping |
| Application industry | Robot industry,Medical industry,Making machine industry,Automation industry,3C industry equipment,Packaging industry,UAV industry,New energy industry. |
| Advantages | 1.High temperature resistance,Self lubrication,Wear resistance,Flame retardant properties 2.Good quality products 3.Competitive prices 4.Fast delivery 5.Best after-sale service 6.Brand: HeFa or OEM/ ODM 7.Good service:satisfactory service before and after sale. 8.Direct manufacturers |
Company Profile
Packaging & Shipping
| lead time | 10-15 working days as usual,30days in busy season,it will based on the detailed order quantity |
| Delivery of samples | by DHL,Fedex,UPS,TNT,EMS |
FAQ
| Main Markets? | North America, South America, Eastern Europe , West Europe , North Europe, South Europe, Asia |
| How to order? | * You send us drawing or sample |
| * We carry through project assessment | |
| * We give you our design for your confirmation | |
| * We make the sample and send it to you after you confirmed our design | |
| * You confirm the sample then place an order and pay us 30% deposit | |
| * We start producing | |
| * When the goods is done, you pay us the balance after you confirmed pictures or tracking numbers. | |
| * Trade is done, thank you!! |
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | Type A |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Surface Treatment: | Natural Color Anodizing,Hard Anodizing |
| Application: | Automation Equipment |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How do flat belt pulleys affect the performance of textile manufacturing machinery?
Flat belt pulleys have a significant impact on the performance of textile manufacturing machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Flat belt pulleys are essential for transmitting power from the motor or engine to various components within textile manufacturing machinery. They serve as driving pulleys, connecting the power source to critical machine parts, such as spindles, rollers, and looms. The efficient power transmission facilitated by flat belt pulleys ensures the smooth operation of these components, enabling the production of high-quality textiles.
2. Speed Control:
Textile manufacturing machinery often requires precise speed control for different processes, such as spinning, weaving, or knitting. Flat belt pulleys, when used in conjunction with adjustable speed drives, allow operators to control the rotational speed of the driven components. By selecting pulleys of different sizes or adjusting the pulley positions, the speed ratios can be modified, enabling optimal machine performance and ensuring the production of textiles with consistent quality.
3. Tensioning and Tracking:
Flat belts in textile manufacturing machinery need to be properly tensioned and tracked to ensure smooth and reliable operation. Flat belt pulleys are equipped with tensioning mechanisms and tracking features to maintain the appropriate belt tension and alignment. Proper tensioning and tracking, facilitated by the pulleys, prevent belt slippage, reduce wear and tear, and minimize the occurrence of defects in textile production.
4. Belt Longevity:
Flat belt pulleys, when designed and maintained correctly, contribute to the longevity of the belts used in textile manufacturing machinery. The pulleys should have smooth surfaces and edges, minimizing friction and wear on the belts. Additionally, regular inspection and maintenance of the pulleys, including checking for proper alignment and cleaning, help prevent belt damage and extend their lifespan.
5. Noise and Vibration Reduction:
Textile manufacturing machinery often operates at high speeds, leading to noise and vibration. Properly balanced and aligned flat belt pulleys help reduce these undesirable effects by ensuring smooth and stable power transmission. Minimizing noise and vibration improves the working environment for operators and helps maintain the integrity of the textile manufacturing process.
6. Maintenance and Replacement:
Flat belt pulleys in textile manufacturing machinery are relatively easy to maintain and replace. Regular inspection and lubrication of the pulleys, along with routine belt tension checks, contribute to efficient operation and prevent unexpected breakdowns. When replacement is necessary, flat belts and pulleys are readily available, minimizing downtime and optimizing overall machine performance.
7. Cost-effectiveness:
Flat belt pulleys offer a cost-effective solution for power transmission in textile manufacturing machinery. They are relatively simple in design, require minimal maintenance, and have lower initial costs compared to alternative transmission systems. The cost-effectiveness of flat belt pulleys makes them a preferred choice in the textile industry.
Overall, flat belt pulleys play a vital role in textile manufacturing machinery by ensuring efficient power transmission, enabling speed control, maintaining belt tension and tracking, enhancing belt longevity, reducing noise and vibration, facilitating maintenance and replacement, and providing a cost-effective solution. Their proper selection, installation, and maintenance are crucial for optimal performance and productivity in textile manufacturing processes.

How does the design of a flat belt pulley affect its performance?
The design of a flat belt pulley plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Groove Profile:
The groove profile of a flat belt pulley affects the grip and traction between the pulley and the belt. Different groove profiles, such as V-shaped, U-shaped, or flat, are used depending on the type of belt being used. The groove profile should be designed to optimize the belt’s contact area and prevent slippage, ensuring efficient power transmission.
2. Diameter and Width:
The diameter and width of the pulley directly impact its mechanical advantage and power transmission capabilities. Larger pulley diameters result in higher belt speeds and increased power transmission capacity, while wider pulleys provide better belt support and reduced belt stress.
3. Material Selection:
The choice of material for the pulley affects its strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Commonly used materials include steel, cast iron, aluminum, and plastics. The material selection should be based on factors such as the load capacity, operating environment, and desired lifespan of the pulley.
4. Balance and Alignment:
A well-designed flat belt pulley should be properly balanced and aligned to minimize vibration and ensure smooth operation. Imbalances or misalignment can result in increased noise, reduced efficiency, and premature wear of the pulley and belt.
5. Tensioning Mechanism:
The design of the tensioning mechanism, such as an idler pulley or tensioning screw, can impact the ease of belt tensioning and the ability to maintain proper belt tension over time. A well-designed tensioning mechanism ensures consistent and reliable power transmission by maintaining the optimal tension in the belt.
6. Flanges and Hub Configuration:
The presence of flanges or the configuration of the hub can affect the stability and alignment of the pulley. Flanges help to keep the belt contained within the pulley, preventing lateral movement and ensuring proper tracking. The hub configuration should provide a secure and accurate connection to the shaft, minimizing slippage or misalignment.
7. Surface Finish and Coating:
The surface finish and coating of the pulley can influence its friction characteristics, wear resistance, and corrosion protection. Smooth surface finishes and appropriate coatings can reduce friction, extend the life of the pulley and belt, and improve overall performance.
By carefully considering and optimizing these design factors, flat belt pulleys can be engineered to deliver efficient and reliable power transmission, minimize belt wear, and ensure long-lasting performance in various applications.

How do flat belt pulleys differ from other types of pulleys?
Flat belt pulleys have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of pulleys. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Belt Type:
The major difference lies in the type of belt used. Flat belt pulleys are specifically designed to work with flat belts, which are flexible and have a rectangular cross-section. In contrast, other types of pulleys, such as V-belt pulleys or timing belt pulleys, are designed for different belt profiles, such as V-shaped belts or toothed belts.
2. Belt Engagement:
Flat belt pulleys engage with the belt differently compared to other pulley types. The flat belt wraps around the pulley’s flat or slightly concave surface and relies on friction to transmit power. Other pulley types, like V-belt pulleys, have grooves that match the shape of the belt, providing positive engagement by fitting into the belt’s grooves.
3. Power Transmission:
Each pulley type is optimized for specific power transmission requirements. Flat belt pulleys are often used for applications that require relatively low power and moderate speeds. They are suitable for machinery that needs flexibility and ease of installation, making them commonly used in older machinery and certain industrial applications. Other pulley types, like V-belt pulleys or timing belt pulleys, offer advantages for high-power transmission, increased efficiency, or precise timing in applications such as automotive engines or industrial machinery.
4. Pulley Design:
Flat belt pulleys have a simple design, typically consisting of a cylindrical or disk-shaped body with a flat or slightly concave surface. Other pulley types may have more complex designs to accommodate specific belt profiles. For example, V-belt pulleys have grooves that match the V-shaped belts, while timing belt pulleys have toothed profiles that match the teeth on the timing belts.
5. Speed and Torque Conversion:
The design and configuration of pulleys, including flat belt pulleys, allow for speed and torque conversion. By varying the sizes of the pulleys, the speed and torque can be adjusted to meet the requirements of the machinery. However, the specific mechanisms for speed and torque conversion may differ between pulley types. For example, V-belt pulleys rely on the varying diameters of the pulleys to achieve speed conversion, while timing belt pulleys use the toothed profiles to ensure precise timing and synchronization.
6. Belt Tension and Alignment:
The methods used to maintain belt tension and alignment can also differ between pulley types. Flat belt pulleys often rely on adjustable pulley positions or tensioning mechanisms to achieve proper tension and alignment. Other pulley types may incorporate features like automatic tensioners or specialized tensioning systems to maintain optimal belt performance.
In conclusion, flat belt pulleys differ from other types of pulleys in terms of the belt type, engagement method, power transmission capabilities, design, speed and torque conversion mechanisms, as well as belt tension and alignment methods. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate pulley type for a given application.


editor by CX
2024-01-24