Product Description
|
Spec |
|
|
Polymer |
NR/SBR |
|
Density |
1.246 |
|
Hardness (Shore A) |
60±5 |
|
Tensile strength (MPA) |
14(≥14) |
|
Elongation (%) |
640(≥400) |
|
Wear (mm3) |
178(≤200) |
|
Tearing strength (N/mm) |
51 |
|
Temp (ºC) |
-40-110 |
Note: Can be produce according the client’s requirement
|
Product No. |
Thickness |
Width |
Length |
|
6832501 |
12/15/20mm |
100-500mm |
1200mm |
|
6832450 |
12/15/20mm |
100-500mm |
1450mm |
|
6832451 |
12/15/20mm |
100-500mm |
1650mm |
|
6832783 |
12/15/20mm |
100-500mm |
1850mm |
|
6832258 |
12/15/20mm |
100-500mm |
2100mm |
|
6832452 |
12/15/20mm |
100-500mm |
10m |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Industrial |
| Feature: | Wear-resistant, Heat-resistant, Corrosion-resistant, Cold-resistant |
| Raw Materials: | Natural Rubber, Pad |
| Medium: | Pure Gum Rubber Sheet and Fabric |
| Performance: | Insulating Rubber Slab |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
Can flat belt pulleys be part of woodworking and milling equipment?
Yes, flat belt pulleys can be an integral part of woodworking and milling equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Flat belt pulleys are commonly used in woodworking and milling equipment to transmit power from a motor or engine to various components. They serve as driving pulleys, connecting the power source to critical machine parts such as saw blades, cutters, drills, or spindles. The efficient power transmission facilitated by flat belt pulleys ensures the smooth and precise operation of these components, enabling accurate woodworking and milling processes.
2. Speed Control:
Woodworking and milling equipment often require adjustable speed control for different tasks and materials. Flat belt pulleys, in combination with adjustable speed drives, allow operators to control the rotational speed of the driven components. By selecting pulleys of different sizes or adjusting the pulley positions, the speed ratios can be modified to match specific cutting or milling requirements, ensuring optimal machine performance and quality of the finished products.
3. Load Capacity:
Woodworking and milling equipment handle various types and sizes of materials, which may exert different loads on the machines. Flat belt pulleys are designed to handle different load capacities based on the specific requirements of the equipment. The pulley’s diameter and width are chosen to provide adequate support and load-bearing capacity for the belt, enabling the machines to handle different workpieces effectively.
4. Belt Tensioning and Tracking:
Proper belt tensioning and tracking are crucial in woodworking and milling equipment to ensure accurate cuts and milling operations. Flat belt pulleys are equipped with tensioning mechanisms and tracking features to maintain the appropriate belt tension and alignment. This helps prevent belt slippage, ensures precise movement of the workpiece, and minimizes the occurrence of errors or defects in the woodworking and milling processes.
5. Versatility:
Flat belt pulleys offer versatility in woodworking and milling equipment design. They can be used in various types of machines, such as table saws, band saws, planers, routers, and milling machines. The flexibility of flat belts also enables efficient movement around pulleys of different sizes and configurations, catering to the specific needs of different woodworking and milling tasks.
6. Durability and Precision:
Woodworking and milling equipment require pulleys that are durable and capable of providing precise power transmission. Flat belt pulleys are often constructed from materials such as cast iron or steel, ensuring strength and longevity. The precision of the pulley design, including accurate machining and balance, contributes to the overall precision of the woodworking and milling processes.
7. Maintenance and Replacement:
Flat belt pulleys in woodworking and milling equipment are relatively easy to maintain and replace. Regular inspection and lubrication of the pulleys, along with routine belt tension checks, contribute to efficient operation and prevent unexpected breakdowns. When replacement is necessary, flat belts and pulleys are readily available, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted woodworking and milling operations.
In summary, flat belt pulleys are commonly incorporated into woodworking and milling equipment to facilitate efficient power transmission, enable speed control, handle varying load capacities, ensure belt tensioning and tracking, offer versatility, provide durability and precision, and allow for easy maintenance and replacement. Their proper selection and maintenance are crucial for achieving high-quality woodworking and milling results.
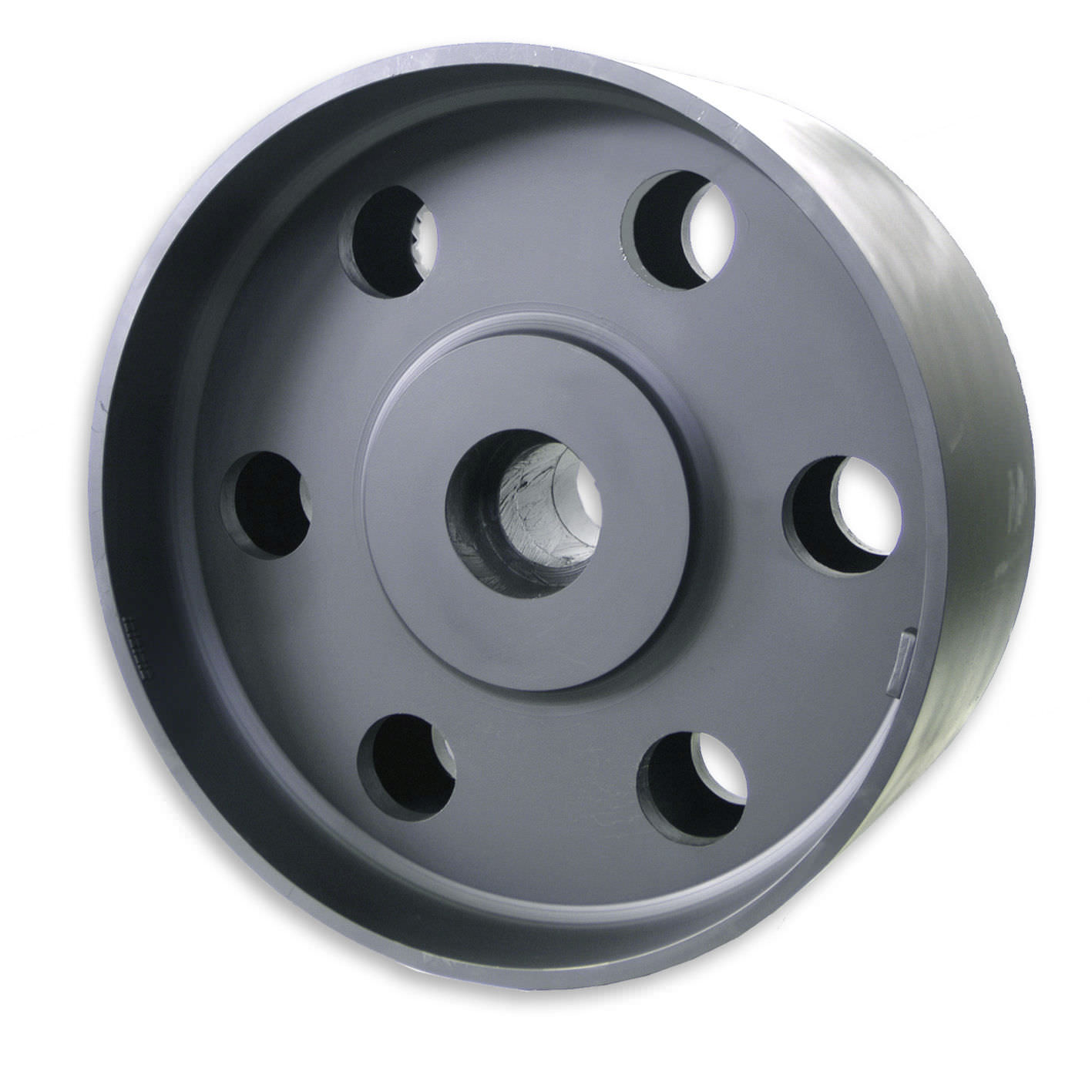

How does the design of a flat belt pulley affect its performance?
The design of a flat belt pulley plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Groove Profile:
The groove profile of a flat belt pulley affects the grip and traction between the pulley and the belt. Different groove profiles, such as V-shaped, U-shaped, or flat, are used depending on the type of belt being used. The groove profile should be designed to optimize the belt’s contact area and prevent slippage, ensuring efficient power transmission.
2. Diameter and Width:
The diameter and width of the pulley directly impact its mechanical advantage and power transmission capabilities. Larger pulley diameters result in higher belt speeds and increased power transmission capacity, while wider pulleys provide better belt support and reduced belt stress.
3. Material Selection:
The choice of material for the pulley affects its strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Commonly used materials include steel, cast iron, aluminum, and plastics. The material selection should be based on factors such as the load capacity, operating environment, and desired lifespan of the pulley.
4. Balance and Alignment:
A well-designed flat belt pulley should be properly balanced and aligned to minimize vibration and ensure smooth operation. Imbalances or misalignment can result in increased noise, reduced efficiency, and premature wear of the pulley and belt.
5. Tensioning Mechanism:
The design of the tensioning mechanism, such as an idler pulley or tensioning screw, can impact the ease of belt tensioning and the ability to maintain proper belt tension over time. A well-designed tensioning mechanism ensures consistent and reliable power transmission by maintaining the optimal tension in the belt.
6. Flanges and Hub Configuration:
The presence of flanges or the configuration of the hub can affect the stability and alignment of the pulley. Flanges help to keep the belt contained within the pulley, preventing lateral movement and ensuring proper tracking. The hub configuration should provide a secure and accurate connection to the shaft, minimizing slippage or misalignment.
7. Surface Finish and Coating:
The surface finish and coating of the pulley can influence its friction characteristics, wear resistance, and corrosion protection. Smooth surface finishes and appropriate coatings can reduce friction, extend the life of the pulley and belt, and improve overall performance.
By carefully considering and optimizing these design factors, flat belt pulleys can be engineered to deliver efficient and reliable power transmission, minimize belt wear, and ensure long-lasting performance in various applications.

How do flat belt pulleys handle variations in load capacity and speed?
Flat belt pulleys are designed to handle variations in load capacity and speed in power transmission systems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Load Capacity:
Flat belt pulleys can accommodate variations in load capacity by adjusting the tension in the flat belt. Increasing the tension in the belt helps to transmit higher loads, while reducing the tension allows for lower loads. The tension can be adjusted by adjusting the position of the pulleys or by using tensioning devices such as idler pulleys or tensioning screws. By properly tensioning the belt, flat belt pulleys can efficiently transmit power and handle different load capacities.
2. Speed Variation:
Flat belt pulleys can handle variations in speed by adjusting the pulley diameters. The speed ratio between the driving pulley and the driven pulley determines the speed at which power is transmitted. By using pulleys with different diameters, the rotational speed can be adjusted accordingly. For example, a larger pulley on the driving shaft and a smaller pulley on the driven shaft will result in increased speed, while a smaller driving pulley and a larger driven pulley will reduce the speed. By selecting the appropriate pulley sizes, flat belt pulleys can accommodate different speed requirements in power transmission systems.
3. Variable Speed Pulleys:
In applications where continuous speed variation is required, variable speed pulleys can be used. These pulleys, also known as stepless or variable pitch pulleys, consist of two conical pulleys that can move axially, changing the effective diameter of the pulley. By adjusting the position of the conical pulleys, the speed ratio can be continuously varied, allowing for precise control of the transmitted speed. Variable speed pulleys are commonly used in applications such as conveyors, fans, and certain types of machinery that require adjustable speeds.
4. Belt Material Selection:
The choice of belt material can also contribute to handling variations in load capacity and speed. Different belt materials possess varying levels of strength, flexibility, and wear resistance. By selecting the appropriate belt material based on the specific application requirements, flat belt pulleys can effectively handle variations in load capacity and speed. For example, high-strength materials may be chosen for heavy-duty applications, while more flexible materials may be suitable for applications with high-speed variations.
It’s important to note that while flat belt pulleys can handle variations in load capacity and speed to a certain extent, there are practical limits based on the design and capabilities of the specific pulley system. It’s crucial to consider the manufacturer’s specifications, operating conditions, and safety factors when determining the suitable load capacity and speed requirements for a flat belt pulley system.


editor by CX
2024-04-23