Product Description
Company Profile
Hongxin is IATF16949 ceritficated and professional in designing and manufacturing molds,producing prototype, precision high-pressure aluminum alloy die casting parts,zinc alloy high-pressure die casting parts, precision CNC parts and precision plastic injection parts.
Product Description
| Technical parameters | Aluminum alloy die casting: ADC12/A360/A380/Alsi9cu3/Alsi12Cu1Fe/Alsi12Fe |
| Zinc alloy die casting:ZA3#,ZA5#,ZA8# | |
| Plastic injection: PA6/PA66/ABS/PC/POM/PE | |
| Aluminum alloy profile extrusion: 6061/6063/6082/7075 | |
| CNC machining and Turnning: 6061/6063/5052 | |
| Part Weight: From 10g to 50000g | |
| Manufacture Process | Drawing/Sample→Mold→Die casting→Deburring → Polishing→CNC Machining→Surface Finishing→ Assembly →Quality Inspection→Packaging→Delivery |
| Equipment | Cold chamber die casting machine:180T/280T/350T/500T/800T/1250T |
| Injection machines: 88T/128T/160T/250T/380T/500T | |
| CNC centers, CNC turning, CNC lathes, electrical pulse, line cutting, milling, drilling, grinding | |
| Surface Treatment | Trimming, Deburring,Polishing, Shot blasting, Sandblasting,Tumbling, Powder coating, Anodizing, Chrome, Electrophoresis, Passivation, Chemical coating |
| Software | Pro-e/Solid work/UG/Auto CAD/CATIA |
| Products Application | Automotive, Electric Motor, Light, Motorcycle,Bicycle, Power tool, Telecommunication, Gas Meter, Home Appliance Equipment, Compressors, Flow Meters, Pumps, Valves, Traffic Equipment, etc. |
Our Advantages
- Direct manufacturer, lower cost and quicker feedback
- Specialist in prototyping, help you fast verify your design
- Specialist in low quantity orders (no MOQ requirement for aluminum CNC parts)
- Specialist in one-step production services from designing to assembly
Facility capability
Samples
FAQ
| Q1. Where is your company? |
| A:Our company is located in HangZhou City, ZHangZhoug province, which is known as the hometown of mold |
| Q2. Are you a factory or trading company? |
| A: We are a direct and professional factory and specialized in die casting industry since 2011. |
| Q3.Can your company make by sample? |
| A: Yes, we can make by both the sample and drawing. |
| Q4. What do I need to provide if I want to customize products and get a offer? |
| A: You can send 2D & 3D drawing(.step/.stp/.igs/.dwg is prefer) or samples and detailed requirement to our team. |
| Q5. What’s the process of Customizing product? |
| A: 1. Design of product drawings/samples. 2. Confirm the drawing with the customer. 3. Make the mold. 4. Send sample to customer for approval. 5. Receive confirmation from customer and series production. 6. Quality inspection 7. Packing and shipping. |
| Q6. Can your company make the mold? |
| A: Yes, design mold and make mold and fixture by ourselves. |
| Q7. Your company’s yearly production capacity? |
| A: 200 set of molds, 5 Million die casting parts and aluminum extrusion parts, 1 Million plastic injection parts |
| Q8. What is the minimum order quantity? |
| A:No MOQ for aluminum CNC parts. Low MOQ can be provided to help you test market. |
| Q9. How long is the lead time? |
| A: Depends on the order quantity. 1 week for prototypes,Normally 3-7 weeks for mold, 2-4 weeks for series production parts. |
| Q10. How do you package the products? |
| A: Bubble bag – Carton Box – Wooden pallet. Special packaging method can be accepted. |
| Q11. What is the payment method? |
| A: T/T, WEST UNION, PAYPAL. |
| Q12.How is the quality? |
| A: Strict control before shipment. |
| Q13: What if I got some defective products? |
| A:If you find any defective products, we will exchange good products or refund you immediately. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Die Casting Machine Type: | Cold Chamber Die Casting Machine |
|---|---|
| Die Casting Method: | Precision Die Casting |
| Application: | Auto Parts |
| Machining: | CNC Machining |
| Material: | Aluminum Alloy |
| Surface Preparation: | Spray Coating |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
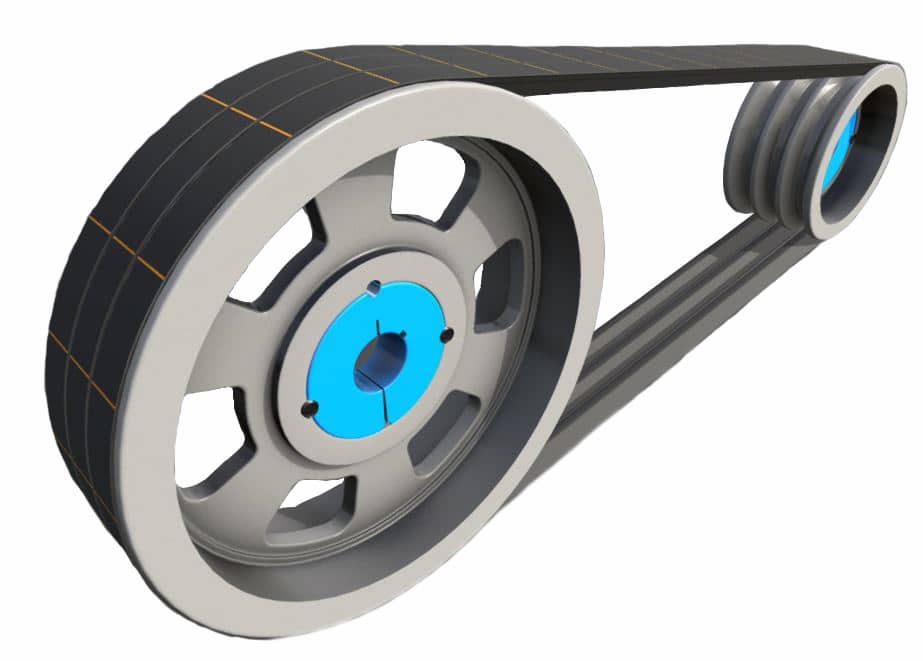
How are belt pulleys utilized in the production of electronics and semiconductors?
In the production of electronics and semiconductors, belt pulleys play a crucial role in various manufacturing processes. They are utilized in different stages of production to facilitate precision, efficiency, and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation of how belt pulleys are utilized in the production of electronics and semiconductors:
1. Conveyor Systems: Belt pulleys are commonly used in conveyor systems within electronics and semiconductor manufacturing facilities. These conveyor systems transport components, products, or wafers between different stages of production, such as assembly, testing, and packaging. Belt pulleys are utilized to drive the conveyor belts, ensuring smooth and controlled movement of the materials or products. They contribute to the efficient flow of production, allowing for continuous and automated handling of electronic components and semiconductor wafers.
2. Wafer Handling: Belt pulley systems are employed in the handling and processing of semiconductor wafers. These wafers, which serve as the base material for electronic devices, need to be transferred between various equipment and processing stations. Belt pulleys, along with precision belts, are used to grip and transport the delicate and flat wafers. The pulleys ensure accurate positioning and controlled movement of the wafers, essential for precise alignment during processes such as etching, deposition, and lithography.
3. Robotics and Automation: Belt pulleys are integral components in robotics and automation systems utilized in electronics and semiconductor production. These systems often involve robotic arms or gantries that handle and manipulate components or equipment. Belt pulleys are employed in the motorization and control mechanisms of these robotic systems, enabling precise and repeatable movements. They contribute to the accuracy, speed, and reliability required in tasks such as pick-and-place operations, soldering, and inspection processes.
4. Precision Machining: Belt pulleys are used in precision machining operations within electronics and semiconductor production. They are incorporated into milling machines, lathes, and other machining equipment that fabricate electronic components and semiconductor parts. Belt pulleys drive the cutting tools or spindles, providing the necessary rotational motion for precise material removal and shaping. The speed control and torque conversion capabilities of belt pulleys ensure the optimal performance and accuracy required for manufacturing intricate electronic and semiconductor components.
5. Testing and Inspection Equipment: Belt pulleys are utilized in testing and inspection equipment within the electronics and semiconductor industry. These machines perform various tests, measurements, and inspections to ensure the quality and functionality of electronic components and semiconductor devices. Belt pulleys drive the mechanisms that move the components or devices through different testing or inspection stations. They contribute to the controlled and synchronized movement required for accurate measurements, functional tests, and quality checks.
6. Packaging and Labeling: Belt pulleys are employed in packaging and labeling systems for electronics and semiconductor products. These systems handle the final packaging of electronic components, devices, or integrated circuits. Belt pulleys drive the conveyor belts that transport the packaged products, ensuring their smooth and efficient movement through the packaging and labeling processes. They contribute to the automated and streamlined packaging operations, allowing for high-speed production and consistent product presentation.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability: Belt pulleys contribute to the maintenance and serviceability of equipment used in electronics and semiconductor production. They are designed for easy replacement, adjustment, or inspection, allowing for quick and straightforward maintenance tasks. Properly maintained belt pulleys ensure the reliability and uptime of production equipment, minimizing downtime and optimizing the overall manufacturing process.
In summary, belt pulleys are utilized in the production of electronics and semiconductors for conveyor systems, wafer handling, robotics and automation, precision machining, testing and inspection equipment, packaging and labeling systems, as well as maintenance and serviceability. They contribute to the efficient flow of production, precise positioning of components, accurate machining, reliable testing and inspection, streamlined packaging, and ease of equipment maintenance. Belt pulleys play a vital role in enhancing the precision, efficiency, and reliability of the manufacturing processes involved in electronics and semiconductor production.

Can belt pulleys be customized for specific machinery and equipment?
Yes, belt pulleys can be customized to meet the specific requirements of machinery and equipment in various applications. Customization allows for the adaptation of belt pulleys to specific dimensions, performance characteristics, and operational needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how belt pulleys can be customized for specific machinery and equipment:
1. Dimensional Customization: Belt pulleys can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the machinery and equipment they will be installed in. This includes customizing the diameter, width, and groove dimensions of the pulleys to ensure proper fit and alignment with the system. Customization ensures that the belt pulleys integrate seamlessly into the machinery, optimizing performance and reliability.
2. Material Selection: Depending on the specific requirements of the machinery and equipment, belt pulleys can be customized with different materials. The choice of materials can be based on factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, chemical resistance, and operating temperature. Common materials used for customized belt pulleys include steel, aluminum, cast iron, and various composites. Custom material selection ensures that the pulleys can withstand the demands of the application.
3. Specialized Coatings and Finishes: In certain applications, customized belt pulleys may require specialized coatings or finishes to enhance their performance. For example, pulleys used in food processing or pharmaceutical industries may require coatings that comply with specific safety and hygiene standards. Customized coatings can also provide corrosion resistance or reduce friction, improving the overall efficiency and longevity of the pulleys.
4. Groove Profiles: Belt pulleys can be customized with specific groove profiles to match the type of belt being used. Different belts, such as V-belts, timing belts, or flat belts, have varying groove requirements. Customizing the groove profiles ensures optimal belt engagement, maximizing power transmission efficiency and preventing belt slippage.
5. Special Features: In some cases, customized belt pulleys may require additional features or modifications to meet specific operational needs. This can include the incorporation of keyways, set screws, flanges, or other attachments to ensure proper alignment and secure mounting. Customized pulleys can also be designed with specific hub configurations or balancing requirements to achieve smooth and balanced operation in the machinery and equipment.
6. Performance Optimization: Customized belt pulleys can be tailored to optimize performance in specific applications. This may involve adjusting the pulley design, such as modifying the number of grooves or altering the pitch diameter, to achieve the desired speed ratios or torque requirements. Performance optimization ensures that the customized pulleys contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of the machinery and equipment.
Overall, belt pulleys can be customized to match the dimensional requirements, material specifications, coating needs, groove profiles, special features, and performance optimization of specific machinery and equipment. Customization ensures that the pulleys seamlessly integrate into the system, providing efficient power transmission and meeting the unique operational needs of the application.

Can you explain the different types of belt pulleys and their applications?
There are several different types of belt pulleys, each designed for specific applications and requirements. The choice of pulley type depends on factors such as the power transmission needs, speed control requirements, space limitations, and the type of belt or rope used. Here’s an overview of some common types of belt pulleys and their applications:
1. V-Belt Pulleys: V-belt pulleys are one of the most widely used types of pulleys. They have a trapezoidal groove profile and are designed to accommodate V-belts, which have a corresponding cross-sectional shape. V-belt pulleys are commonly used in applications that require high torque transmission, such as in industrial machinery, automotive engines, and HVAC systems.
2. Flat Belt Pulleys: Flat belt pulleys have a flat or slightly crowned surface without any grooves. They are used with flat belts, which have a rectangular cross-section. Flat belt pulleys are suitable for applications that require high-speed power transmission, such as in textile machines, printing presses, and conveyor systems.
3. Timing Belt Pulleys: Timing belt pulleys, also known as synchronous pulleys, have teeth or grooves that mesh with the teeth of a timing belt. This design provides precise and synchronous power transmission, making them suitable for applications that require accurate positioning and timing, such as in robotics, CNC machines, and automotive engines.
4. Variable Speed Pulleys: Variable speed pulleys, also called adjustable or variable pitch pulleys, allow for continuous speed control by adjusting the effective diameter of the pulley. They feature movable pulley halves or arms that change the distance between the grooves, altering the speed ratio. Variable speed pulleys are used in applications where adjustable speed control is required, such as in machinery with variable loads or in variable speed drives.
5. Step Pulleys: Step pulleys have multiple grooves of different diameters arranged on the same pulley. By changing the belt position between these different grooves, the speed ratio can be adjusted. Step pulleys are commonly used in machines such as drill presses, lathes, and milling machines, where a range of predetermined speeds is required for different operations.
6. Idler Pulleys: Idler pulleys are not directly involved in power transmission but are used to redirect and tension the belt. They help maintain proper belt tension, improve belt wrap around the pulleys, and assist in achieving the desired belt path. Idler pulleys are commonly used in automotive engines, HVAC systems, and other belt-driven systems.
7. Clutch Pulleys: Clutch pulleys are specialized pulleys that incorporate a clutch mechanism. They allow for on-demand engagement and disengagement of the pulley from the driven shaft. Clutch pulleys are commonly used in automotive applications, such as in alternators, where they enable efficient power generation while reducing drag during idle or deceleration.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of belt pulley types, and there may be other specialized designs based on specific application requirements. The selection of the appropriate belt pulley type depends on factors such as the power transmission needs, speed control requirements, load capacity, and the type of belt or rope used.
In summary, different types of belt pulleys, such as V-belt pulleys, flat belt pulleys, timing belt pulleys, variable speed pulleys, step pulleys, idler pulleys, and clutch pulleys, are designed for specific applications and requirements. Understanding the characteristics and applications of these pulley types allows for the proper selection and utilization of belt pulleys in various mechanical systems.


editor by CX
2024-05-07