Product Description
Head Drive Pulley, Return Pulley,Bend Pulley, Snub Pulley,Tensioning Pulley, Take up Pulley can be provided. We are designing and manufacturing pulleys, using materials of the highest quality in a production process employing advanced technology. This together with the application of the Quality Assurance system certifi ed to ISO 9001:2015, contributes to the production of high quality products offering dependable, long life performance in the field and appreciably reducing maintenance cost. Each our conveyor pulley is individually computer designed to meet the client’s requirements.
|
Product Name |
Belt Conveyor Pulley Drum |
||
|
Type |
Drive Pulley, Bend Pulley,Snub Pulley,Take Up Pulley | ||
|
Length |
200mm-2500mm |
||
|
Materials |
Carbon steel, Stainless steel, Rubber |
||
|
Surface Treatment |
Smooth, CHINAMFG grooved lagging, Herringbone lagging, Ceramic lagging |
||
|
Welding |
Submerged Arc Welding |
||
|
Bearing |
Famous brands |
||
|
Structure |
Tube,shaft,self-aligning bearing,bearing seat/house,hub, locking bushing,end disc |
||
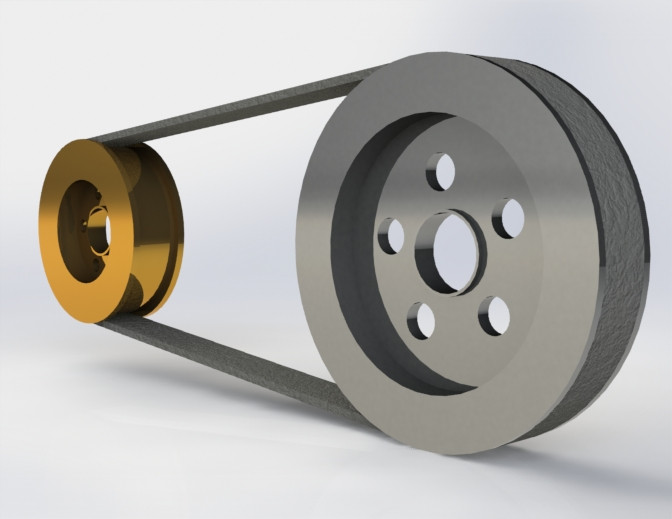
Drive Pulley Introduction:
1. Head/Drive Pulley is located at the discharge terminus of the conveyor.
2. Drive pulley provides the driving force for the conveyor. In order to increase pulley life and traction, it often has a larger diameter than other pulleys.
3. We can supply pulleys with hot vulcanized rubber lagging, plain or grooved, as required by client. Different patterns of grooving such as herringbone or CHINAMFG can be provided to increase tractive friction under dirty or wet conditions. CHINAMFG grooves have the advantage of being installed in any orientation, regardless of belt direction.
Specification of Drive Head Pulley Drum
| Belt Width | 500-2800mm (19-110 inch) |
| Pulley Length | 500-3500mm (19-138 inch) |
| Diameter | 200-1800mm (8-70 inch) |
| Standard | ISO9001:2008, CEMA, DIN, TUV, JIS, AS/NS, etc. |
| Working Life | More than 30,000 hours. |
| Surface | Flat Rubber Lagged, Ceramic Lagged, CHINAMFG Rubber Lagged, etc. |
| Main Material | Carbon Steel |
| Length of conveyor drive pulley depends on the width of conveyor Belt. You can get drive pulleys with hot & cold vulcanized rubber lagging, plain or grooved, as required by client. | |
Bend Pulley Introduction:
1. The bend pulley is used for changing the direction of the belt.
2. The bend pulley is usually installed at the tail part or the vertical take-up equipment part when the belt direction need to 180°bending. It will be installed above the take-up equipment part while 90°bending.
3. The pulley, which is used for extending the contact surface, is usually used for below or equal to 45 degree bending.
4. The surface treatment of the bend pulley can be smooth steel and flat rubber lagging.
Specification of Bend Pulley:
| Belt Width | 500-2800mm(19-110 inch) |
| Pulley Length | 500-3200mm(19-126 inch) |
| Diameter | 200-1800mm(8-70 inch) |
| Standard | ISO9001:2008, CEMA, DIN, TUV, etc. |
| Working Life | More than 30,000 hours. |
| Surface | Flat Rubber Lagged, Ceramic Lagged, CHINAMFG Rubber Lagged, etc. |
| Main Material | Carbon Steel |
| Length of conveyor bend pulley depends on the width of conveyor Belt. You can get drive pulleys with hot vulcanized rubber lagging, plain or grooved, as required by client. | |
Snub Pulley
Snub pulley is used to achieve higher angle of wrap on the drive pulley thereby increasing the traction. It also reduces the belt tension maximizing the life of the conveyor component.It is mounted close to the drive pulley on the return side of the belt.
Specification of Snub Pulley:
| Items | Content |
| Belt Width | 500-2800mm (19-110 inch) |
| Pulley Length | 500-3200mm (19-126 inch) |
| Diameter | 200-1800mm (8-70 inch) |
| Standard | ISO9001:2008, CEMA, DIN, TUV, etc. |
| Working Life | More than 30,000 hours. |
| Surface | Flat Rubber Lagged, Ceramic Lagged, CHINAMFG Rubber Lagged, etc. |
| Main Material | Carbon Steel |
| Length of conveyor Snubpulley depends on the width of conveyor Belt. You can get Snubpulleys with hot vulcanized rubber lagging, plain or grooved, as required by client. | |
Take Up Pulley
The take up pulley will ensure adequate tension of the belt leaving the drive pulley so as to avoid any slippage of the belt, ensure proper belt tension at the loading and other points along the conveyor, compensate for changes in belt length due to elongation, and provide extra length of belt when necessary for splicing purpose.
Specification of take up pulley drum:
| Belt Width | 500-2800mm(19-110 inch) |
| Pulley Length | 500-3200mm(19-126 inch) |
| Diameter | 200-1800mm(8-70 inch) |
| Standard | ISO9001:2008, CEMA, DIN, TUV, etc. |
| Working Life | More than 30,000 hours. |
| Surface | Flat Rubber Lagged, Ceramic Lagged, CHINAMFG Rubber Lagged, etc. |
| Main Material | Carbon Steel |
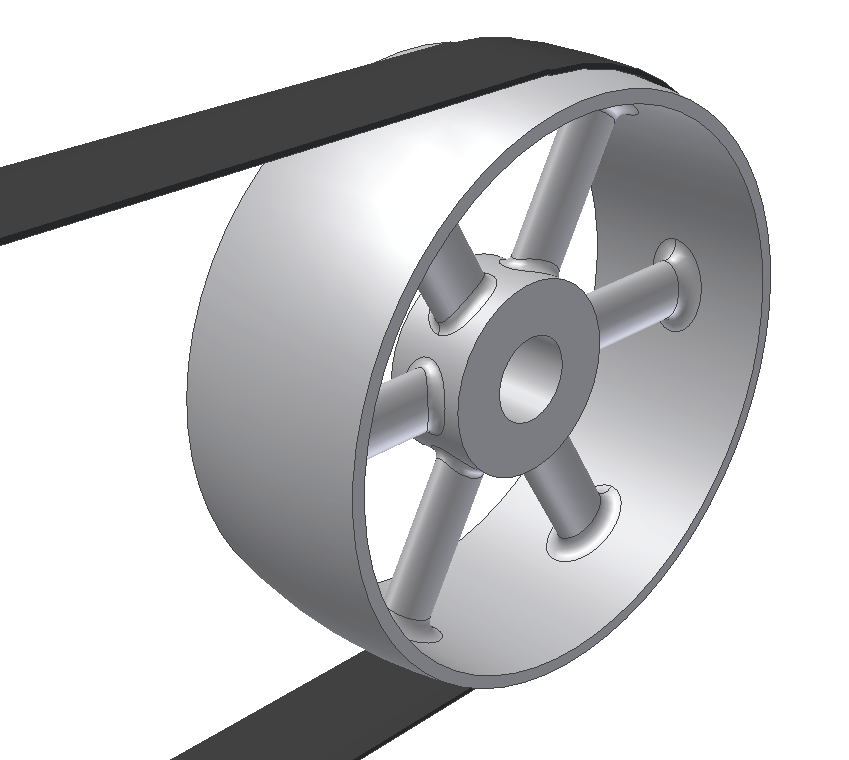
The components of a pulley drum include the following:
| Drum or Shell | The drum is the portion of the pulley in direct contact with the belt. The shell is fabricated from either a rolled sheet of steel or from hollow steel tubing.The shell has a specific ‘face’ width and diameter which is determined by the width of the belting and the type and rating of the belt to be used on the conveyor. | |
| Diaphragm Plates | The diaphragm or end plates of a pulley are circular discs which are fabricated from thick steel plate and which are welded into the shell at each end, to strengthen the drum.The end plates are bored in their centre to accommodate the pulley shaft and the hubs for the pulley locking elements. | |
| Shaft | The shaft is designed to accommodate all the applied forces from the belt and / or the drive unit, with minimum deflection.The shaft is located and locked to the hubs of the end discs by means of a locking elements. The shaft is supported on both ends by bearings which are housed in plummer blocks, to support the shaft and pulley assembly on the conveyor structure. Shafts often comprise different diameters along their length due to the bending moments and resultant deflection limitations. The diameter of the shaft at the landings for the bearings may be smaller to satisfy the necessary bearing diameter which is more cost-effective (smaller). Similarly in the case of a drive shaft, the drive attachment, may be different to the other diameters along the shaft and hence pulley shafts are often stepped. |
|
| Locking Elements | These are high-precision manufactured items which are fitted over the shaft and into the pulley hubs. The locking elements attach the pulley firmly to the shaft via the end plates.Locking elements work on the friction-grip principle whereby the element is able to be fastened to the shaft and hub simultaneously and concentrically, by tightening a series of screws around the locking element. | |
| Hubs | The hubs are fabricated and machined housings which are welded into the end plates. The hubs are sized according to the size of the pulley, the diameter of the shaft and the size of the locking element which is required for the specific duty. | |
| Lagging | It is sometimes necessary or desirable to improve the friction between the conveyor belt and the pulley in order to improve the torque that can be transmitted through a drive pulley.Improved traction over a pulley also assists with the training of the belt. In such cases pulley drum surfaces are ‘lagged’ or covered in a rubberized material. This cover is usually 8 mm to 12 mm thick and can be plain or have a grooved pattern. The rubber lagging is vulcanized to the pulley shell to ensure that it remains attached under adverse operating conditions. |
|
| Bearing Assemblies | Bearings support the rotating shaft and hence the pulley. The bearings are housed in ‘plummer blocks’ which enable the mass of the pulley assembly plus the belt tension forces to be transmitted to the pulley supporting structure.Plummer blocks are often bolted to ‘sole plates’ which are welded to the structure. The sole plates incorporate jacking screws to enable the pulley to be correctly and relatively easily aligned. |
|
Several types of bearing housing, seals and end disc:
Pulley Drum Warehouse and package:
Pulley Drums:
Our Products: Belt Conveyors, Pulley Drum, Conveyor Rollers Idler, etc.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Surface Treatment: | Polishing |
| Motor Type: | Frequency Control Motor |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
How do flat belt pulleys affect the performance of textile manufacturing machinery?
Flat belt pulleys have a significant impact on the performance of textile manufacturing machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Flat belt pulleys are essential for transmitting power from the motor or engine to various components within textile manufacturing machinery. They serve as driving pulleys, connecting the power source to critical machine parts, such as spindles, rollers, and looms. The efficient power transmission facilitated by flat belt pulleys ensures the smooth operation of these components, enabling the production of high-quality textiles.
2. Speed Control:
Textile manufacturing machinery often requires precise speed control for different processes, such as spinning, weaving, or knitting. Flat belt pulleys, when used in conjunction with adjustable speed drives, allow operators to control the rotational speed of the driven components. By selecting pulleys of different sizes or adjusting the pulley positions, the speed ratios can be modified, enabling optimal machine performance and ensuring the production of textiles with consistent quality.
3. Tensioning and Tracking:
Flat belts in textile manufacturing machinery need to be properly tensioned and tracked to ensure smooth and reliable operation. Flat belt pulleys are equipped with tensioning mechanisms and tracking features to maintain the appropriate belt tension and alignment. Proper tensioning and tracking, facilitated by the pulleys, prevent belt slippage, reduce wear and tear, and minimize the occurrence of defects in textile production.
4. Belt Longevity:
Flat belt pulleys, when designed and maintained correctly, contribute to the longevity of the belts used in textile manufacturing machinery. The pulleys should have smooth surfaces and edges, minimizing friction and wear on the belts. Additionally, regular inspection and maintenance of the pulleys, including checking for proper alignment and cleaning, help prevent belt damage and extend their lifespan.
5. Noise and Vibration Reduction:
Textile manufacturing machinery often operates at high speeds, leading to noise and vibration. Properly balanced and aligned flat belt pulleys help reduce these undesirable effects by ensuring smooth and stable power transmission. Minimizing noise and vibration improves the working environment for operators and helps maintain the integrity of the textile manufacturing process.
6. Maintenance and Replacement:
Flat belt pulleys in textile manufacturing machinery are relatively easy to maintain and replace. Regular inspection and lubrication of the pulleys, along with routine belt tension checks, contribute to efficient operation and prevent unexpected breakdowns. When replacement is necessary, flat belts and pulleys are readily available, minimizing downtime and optimizing overall machine performance.
7. Cost-effectiveness:
Flat belt pulleys offer a cost-effective solution for power transmission in textile manufacturing machinery. They are relatively simple in design, require minimal maintenance, and have lower initial costs compared to alternative transmission systems. The cost-effectiveness of flat belt pulleys makes them a preferred choice in the textile industry.
Overall, flat belt pulleys play a vital role in textile manufacturing machinery by ensuring efficient power transmission, enabling speed control, maintaining belt tension and tracking, enhancing belt longevity, reducing noise and vibration, facilitating maintenance and replacement, and providing a cost-effective solution. Their proper selection, installation, and maintenance are crucial for optimal performance and productivity in textile manufacturing processes.

Can flat belt pulleys be customized for specific machinery and equipment?
Yes, flat belt pulleys can be customized to suit specific machinery and equipment requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Pulley Dimensions:
Flat belt pulleys can be customized in terms of their dimensions to fit the specific space and clearance constraints of the machinery or equipment. The outer diameter, inner diameter, and width of the pulley can be adjusted to ensure proper alignment and fit within the system.
2. Shaft Compatibility:
Customized flat belt pulleys can be designed to match the shaft size and configuration of the machinery or equipment. This ensures a secure and accurate connection between the pulley and the shaft, minimizing any potential slippage or misalignment issues.
3. Material Selection:
The choice of material for the pulley can be customized based on the specific requirements of the machinery or equipment. Different materials, such as steel, aluminum, or plastic, offer varying levels of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. The material selection can be tailored to suit factors such as the operating environment, load capacity, and desired longevity of the pulley.
4. Keyways and Set Screw Holes:
Customized flat belt pulleys can be manufactured with keyways or set screw holes to enhance the connection and torque transfer between the pulley and the shaft. Keyways provide a positive locking mechanism, preventing rotational slippage, while set screw holes allow for secure fastening using set screws.
5. Surface Coatings:
In certain cases, customized flat belt pulleys can be coated or treated with specific surface finishes or coatings. These coatings can provide benefits such as improved wear resistance, reduced friction, or enhanced corrosion protection, depending on the operating conditions and requirements of the machinery or equipment.
6. Special Features:
Customized flat belt pulleys can incorporate special features or modifications based on the unique needs of the machinery or equipment. This may include additional mounting holes, balancing adjustments, or specific groove profiles to accommodate different belt types or configurations.
By working with pulley manufacturers or suppliers, machinery or equipment manufacturers can collaborate to design and produce customized flat belt pulleys that precisely meet the requirements of their specific applications.
It’s important to note that the customization process will depend on factors such as the complexity of the pulley design, production feasibility, and any minimum order quantities that may be required by the manufacturer.
What is a flat belt pulley, and how does it function in machinery?
A flat belt pulley is a type of pulley used in machinery that utilizes a flat belt for power transmission. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Design and Construction:
A flat belt pulley consists of a cylindrical or disk-shaped body with a flat or slightly concave surface. It is typically made of durable materials such as cast iron, steel, or aluminum. The pulley may have one or more grooves or channels on its surface to accommodate the flat belt, ensuring proper engagement and power transfer.
2. Power Transmission:
The primary function of a flat belt pulley is to transmit power from a driving source, such as an engine or motor, to a driven component in machinery. The flat belt connects the driving pulley (also known as the driver) to the driven pulley (also known as the driven). As the driving pulley rotates, it imparts rotational motion to the flat belt, which in turn transfers the power to the driven pulley. This enables the driven component to perform its intended function.
3. Belt Grip and Traction:
A flat belt pulley provides grip and traction on the flat belt, ensuring efficient power transfer and minimizing slippage. The design of the pulley surface, including any grooves or channels, helps maintain proper belt engagement and prevents the belt from slipping or coming off the pulley during operation. The pulley’s material and surface finish are chosen to optimize friction and traction between the pulley and the belt.
4. Speed and Torque Conversion:
By varying the size of the flat belt pulleys in a machinery system, the rotational speed and torque can be converted according to the desired requirements. The ratio of the pulley diameters determines the speed ratio between the driving and driven components. For example, a larger pulley on the driving side and a smaller pulley on the driven side will result in increased speed at the driven component but reduced torque. This allows for the customization and adaptation of machinery to different operational needs.
5. Tension and Alignment:
A flat belt pulley aids in maintaining proper tension and alignment of the flat belt. Tensioning mechanisms, such as adjustable pulley positions or tensioners, are utilized to ensure optimal tension in the belt. Proper tension prevents slippage and ensures the belt remains tightly engaged with the pulleys. Additionally, flat belt pulleys may incorporate features like crowned surfaces or tracking guides to aid in belt alignment, reducing the risk of misalignment and optimizing power transmission.
6. Maintenance and Replacement:
Regular maintenance and inspection of flat belt pulleys are essential for their proper functioning. It is important to check for wear, damage, or misalignment of the pulley and the flat belt. Any worn or damaged pulleys should be replaced promptly to prevent performance issues and potential failures in the machinery.
In summary, a flat belt pulley is a key component in machinery for power transmission using flat belts. It provides grip and traction, facilitates speed and torque conversion, aids in tension and alignment, and requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.


editor by CX
2024-05-15