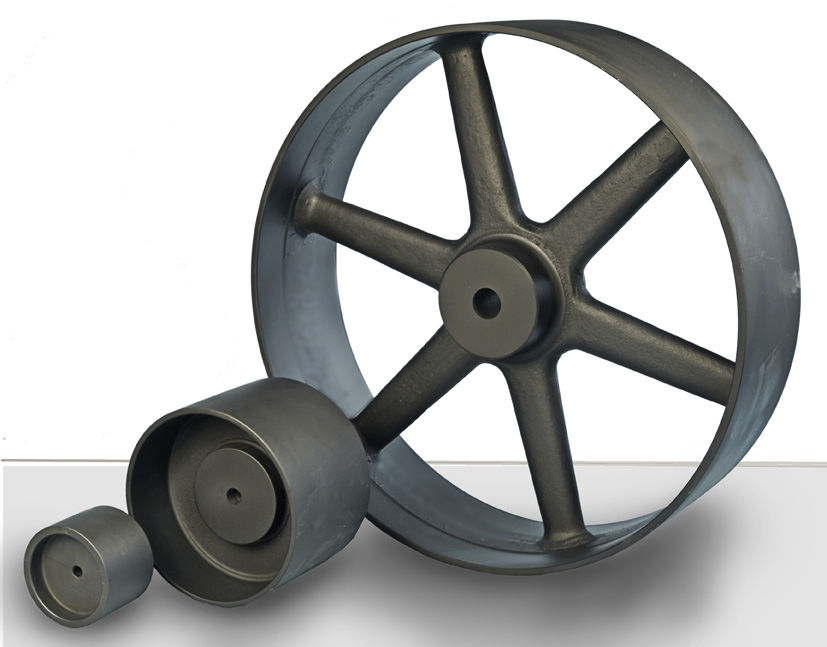
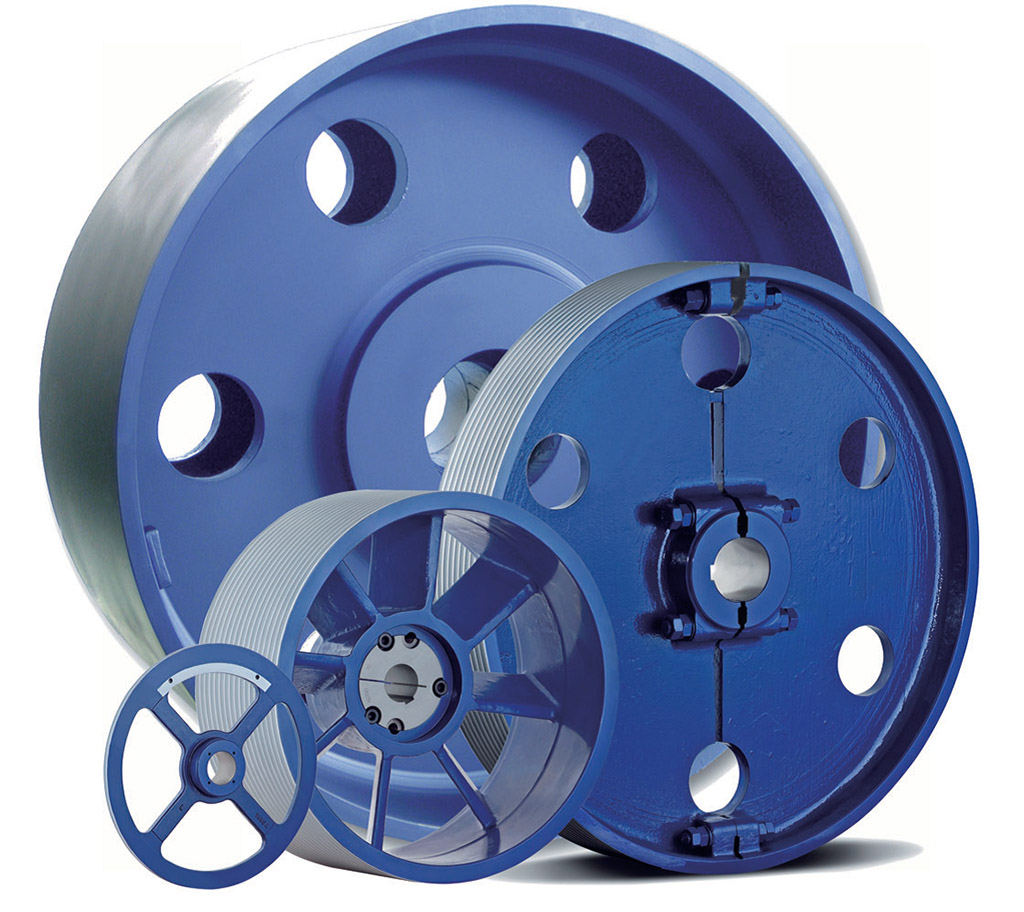
Product Description
Product Description
Product Parameters
| Parameter of conveyor drum pulley | |||
| Type | Belt width | Standard diameter | Length(mm) |
| (mm) | (mm) | ||
| Length of pulley depends on the width of conveyor belt | 500 | 500 | Length of pulley
depends on the width of conveyor belt |
| 650 | 500~630 | ||
| 800 | 630~1000 | ||
| 1000 | 800~1150 | ||
| 1200 | 800~1150 | ||
| 1400 | 1000~1350 | ||
| 1600 | 1150~1600 | ||
| 1800 | 1150~1800 | ||
| 2000 | 1350~2000 | ||
| 2200 | 1600~2200 | ||
| 2400 | 1800~2400 | ||
Production Workshop
Application scenario
Our Advantages
FAQ
Q1. When can I get the price?
Usually we quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry.
Q2: Could design and drawing the pulley for our special usage?
A: Of course, our professional engineer could design and drawing for you ASAP.
Q3:How to install the Ceramic Pulley Lagging?
A:We have experience of installation for 20 years, and could supply guidance for you by video.
Q4: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q5: Do you have foreign experience for Ceramic Pulley Lagging rubber sheet?
A: Yes, the ceramic lagging rubber sheet we manufactured have exported to Australia , South Africa , Brazil , etc.
Q6. How does your factory of regarding quality control?
A: To make sure customer buy good quality material and service from us. Before customer place order, we will send drawing to customer for approval. Before shipment, our QC staff will check quality 1pc by 1pc. Quality is our culture. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Surface Treatment: | Baking Paint |
| Motor Type: | Frequency Control Motor |
| Samples: |
US$ 70/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can flat belt pulleys be integrated into conveyor systems for material handling?
Yes, flat belt pulleys can be effectively integrated into conveyor systems for material handling. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Conveyor systems are widely used in industries for the efficient movement of materials from one location to another. Flat belt pulleys offer several advantages when incorporated into conveyor systems:
1. Power Transmission:
Flat belt pulleys are used as the driving pulleys in conveyor systems. They transmit power from a motor or an engine to the belt, enabling the movement of materials along the conveyor. The large contact area and grip between the pulleys and the belt ensure efficient power transfer, allowing for the transportation of various types of materials.
2. Load Capacity:
Flat belt pulleys are designed to handle different load capacities. They can be selected based on the specific requirements of the conveyor system, such as the weight and type of materials being transported. The pulley’s diameter and width are chosen to provide adequate support and load-bearing capacity for the belt.
3. Belt Tracking:
Proper belt tracking is crucial in conveyor systems to prevent belt misalignment and ensure smooth operation. Flat belt pulleys are designed with features such as flanges or guides to help keep the belt centered and aligned. This ensures that the materials are conveyed along the desired path without any disruptions or spillage.
4. Belt Tensioning and Adjustability:
Flat belt pulleys in conveyor systems are equipped with tensioning mechanisms to maintain the appropriate belt tension. These mechanisms, such as idler pulleys or tensioning screws, allow for easy adjustment of the belt tension to accommodate variations in load or belt stretch over time. Proper tensioning ensures efficient power transmission and prevents belt slippage.
5. Versatility:
Flat belt pulleys offer versatility in conveyor system design. They can be used in straight conveyors, curved conveyors, or inclined conveyors, allowing for the transportation of materials in various directions and angles. The flexibility of flat belts also enables efficient movement around pulleys of different sizes and configurations.
6. Maintenance and Replacement:
Flat belt pulleys in conveyor systems are relatively easy to maintain and replace. Regular inspection and maintenance of the pulleys, including checking for proper alignment and tension, can help prevent issues and ensure efficient operation. When replacement is necessary, flat belts and pulleys are readily available, minimizing downtime and optimizing material handling efficiency.
Consequently, flat belt pulleys are commonly integrated into conveyor systems for material handling due to their efficient power transmission, load capacity, versatility, and ease of maintenance. They are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, warehousing, mining, agriculture, and logistics.
What types of materials are commonly used for flat belt pulley components?
Flat belt pulleys are typically composed of various materials for different components to meet specific requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Pulley Body:
The main body of a flat belt pulley is commonly made of durable and rigid materials such as:
- Steel: Steel pulleys offer excellent strength, durability, and resistance to wear. They are commonly used in heavy-duty applications where high load capacities and long service life are required.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron pulleys are known for their high strength and resistance to wear. They are often used in industrial applications where durability and reliability are essential.
- Aluminum: Aluminum pulleys are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where weight reduction is a priority or in environments where corrosion is a concern.
- Plastics: Certain types of plastics, such as nylon or polyurethane, are used in pulleys where low weight, noise reduction, or chemical resistance is required. Plastic pulleys are often used in applications that involve delicate or sensitive machinery.
2. Hub:
The hub of a flat belt pulley, which connects the pulley to the shaft, is typically made of:
- Steel: Steel hubs offer high strength and reliable connection to the shaft. They are commonly used in heavy-duty applications.
- Aluminum: Aluminum hubs are lightweight and provide good corrosion resistance. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is important.
3. Surface Coating:
To enhance the performance and durability of flat belt pulleys, surface coatings or treatments may be applied. Some common coatings include:
- Zinc or Nickel Plating: These coatings provide corrosion resistance and improve the pulley’s appearance.
- Anodizing: Anodized coatings on aluminum pulleys increase their resistance to wear and corrosion.
- Powder Coating: Powder coating provides a durable and protective layer on the pulley surface, offering improved aesthetics and resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and abrasion.
It’s important to select the appropriate materials for flat belt pulleys based on factors such as the application’s load requirements, environmental conditions, desired lifespan, and cost considerations. Consulting with pulley manufacturers or suppliers can help in determining the most suitable materials for specific pulley components.

How do flat belt pulleys differ from other types of pulleys?
Flat belt pulleys have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of pulleys. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Belt Type:
The major difference lies in the type of belt used. Flat belt pulleys are specifically designed to work with flat belts, which are flexible and have a rectangular cross-section. In contrast, other types of pulleys, such as V-belt pulleys or timing belt pulleys, are designed for different belt profiles, such as V-shaped belts or toothed belts.
2. Belt Engagement:
Flat belt pulleys engage with the belt differently compared to other pulley types. The flat belt wraps around the pulley’s flat or slightly concave surface and relies on friction to transmit power. Other pulley types, like V-belt pulleys, have grooves that match the shape of the belt, providing positive engagement by fitting into the belt’s grooves.
3. Power Transmission:
Each pulley type is optimized for specific power transmission requirements. Flat belt pulleys are often used for applications that require relatively low power and moderate speeds. They are suitable for machinery that needs flexibility and ease of installation, making them commonly used in older machinery and certain industrial applications. Other pulley types, like V-belt pulleys or timing belt pulleys, offer advantages for high-power transmission, increased efficiency, or precise timing in applications such as automotive engines or industrial machinery.
4. Pulley Design:
Flat belt pulleys have a simple design, typically consisting of a cylindrical or disk-shaped body with a flat or slightly concave surface. Other pulley types may have more complex designs to accommodate specific belt profiles. For example, V-belt pulleys have grooves that match the V-shaped belts, while timing belt pulleys have toothed profiles that match the teeth on the timing belts.
5. Speed and Torque Conversion:
The design and configuration of pulleys, including flat belt pulleys, allow for speed and torque conversion. By varying the sizes of the pulleys, the speed and torque can be adjusted to meet the requirements of the machinery. However, the specific mechanisms for speed and torque conversion may differ between pulley types. For example, V-belt pulleys rely on the varying diameters of the pulleys to achieve speed conversion, while timing belt pulleys use the toothed profiles to ensure precise timing and synchronization.
6. Belt Tension and Alignment:
The methods used to maintain belt tension and alignment can also differ between pulley types. Flat belt pulleys often rely on adjustable pulley positions or tensioning mechanisms to achieve proper tension and alignment. Other pulley types may incorporate features like automatic tensioners or specialized tensioning systems to maintain optimal belt performance.
In conclusion, flat belt pulleys differ from other types of pulleys in terms of the belt type, engagement method, power transmission capabilities, design, speed and torque conversion mechanisms, as well as belt tension and alignment methods. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate pulley type for a given application.


editor by CX
2024-03-28